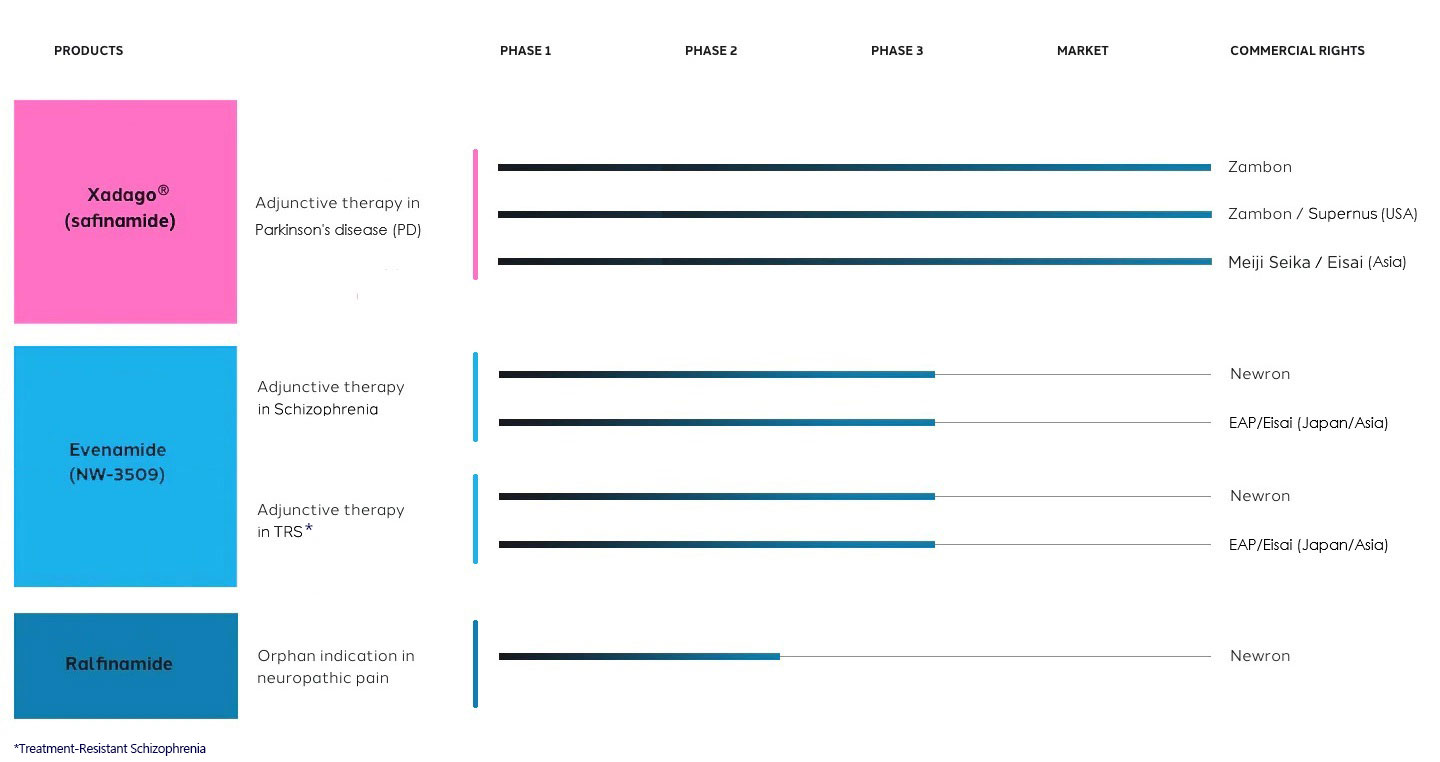
Pipeline
Innovative Clinical Pipeline with Near-Term Catalysts
Evenamide – a potential new treatment paradigm in schizophrenia:
Evenamide is a new oral chemical entity being developed by Newron as an add-on therapy to existing antipsychotics for two difficult-to-treat patient populations:
=> Treatment-resistant schizophrenia (TRS)
=> Chronic schizophrenia with poor response to standard treatment
Evenamide is a novel antipsychotic drug with a unique mechanism of action, distinct from existing treatments. It selectively inhibits voltage-gated sodium channels in hyper-active neurons, leading to normalization of the glutamatergic dysfunction—a key factor in patients who do not respond well to traditional antipsychotic medications. By reducing hippocampal and cortical hyper-excitability, evenamide directly addresses the root cause of the dysfunction. This action restores neurophysiological balance without interfering with over 150 receptors, enzymes, or transporters involved in CNS activity.
Clinical results have demonstrated that adding evenamide to a course of treatment in patients who are inadequately responding to their current therapies provides additional efficacy benefit turns out into with no relevant additional side effects.
Robust clinical data support evenamide’s potential:
- In the one-year Phase II clinical study 014/15, evenamide as add-on therapy to antipsychotics in TRS demonstrated sustained, progressive, and clinically significant improvements across key efficacy measures. These included the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS), Clinical Global Impression of Severity (CGI-S), and Level of Functioning (LOF). Over 70% of patients were showing reduced disease severity and 25% achieving remission – unprecedented in TRS. Remarkably, no patient relapsed during the study, and nearly 50% of patients were no longer considered to have TRS after one year of treatment.
- In the potentially pivotal four-week Phase II/III study 008A, evenamide, added to second-generation antipsychotics, significantly improved symptoms in patients with chronic schizophrenia inadequately responding to current treatments. The study met both its primary (PANSS total score) and key secondary (CGI-S) endpoints. It showed statistically significant benefits, confirming evenamide’s favorable safety and tolerability profile. 008A was also the first randomized, placebo-controlled, and adequately designed study to demonstrate the benefits of a glutamate modulator as an adjunct to atypical antipsychotics.
Phase III development program with Evenamide: ongoing “EveNamIde’s Glutamate Modulation Ameliorates TRS” – ENIGMA-TRS
The ENIGMA-TRS Phase III development program consists of two pivotal studies, ENIGMA-TRS 1 and ENIGMA-TRS 2. The two studies are expected to meet the ICH (International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use) specified regulatory requirements by the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) for submission of the registration dossier for evenamide in major territories, including the US and Europe.
ENIGMA-TRS 1 is a 52-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, international Phase III study evaluating the efficacy, tolerability, and safety of the 15mg BID and 30mg BID therapeutic doses of evenamide compared to placebo. Patients on second-generation anti-psychotics (SGAs), including clozapine, will meet Treatment Response and Resistance Psychosis (TRRIP) international consensus criteria for TRS.
ENIGMA-TRS 1 will enroll at least 600 patients at study centers in Europe, Asia, Latin America, and Canada. Patients will undergo a 42-day screening period, during which their TRS diagnosis, antipsychotic plasma levels (background medication), and conformance to protocol selection criteria will be evaluated by an Independent Eligibility Assessment Committee (IEAC) of three leading international schizophrenia experts.
The primary assessment of efficacy and safety will be performed 12 weeks after randomization to treatment. The study will continue double-blind and placebo-controlled until the 52-week (i.e. one year) time point.
ENIGMA-TRS 2, approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), will be performed at centers in the US and selected additional countries and will include at least 400 patients in a 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled international Phase III study, designed to evaluate the efficacy, tolerability, and safety of the 15mg BID dose of evenamide. Patients will meet selection criteria and be reviewed by the above mentioned IEAC. The analysis for determination of efficacy and safety will be performed after patients complete 12 weeks of participation in the trial.
New Preclinical Study Highlights Evenamide’s Potential to Address Core Schizophrenia Symptoms
New research published in Neuropsychopharmacology demonstrates that evenamide, Newron’s first-in-class glutamate modulator in Phase III development for treatment-resistant schizophrenia, improved positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms in the validated neurodevelopmental MAM model of schizophrenia.
Study results from the University of Pittsburgh show how evenamide, a selective voltage-gated sodium channel blocker, selectively inhibited hyperactive neurons and reduced pyramidal neuron hyperactivitiy in the hippocampus. Additionally, time-course analysis indicated effects of a single dose of evenamide lasted long after its elimination, suggesting evenamide may impact on neuronal plasticity.
These findings suggest for the first time that evenamide’s efficacy in downregulating the hyperdopaminergic state, social deficits, and recognition memory impairment may result from its ability to attenuate hippocampal hyperexcitability and, thus, support the therapeutic relevance of evenamide’s glutamate-modulating mechanism.
The results help explain the robust and sustained symptom improvements observed in Newron’s Phase II and Phase III trials in patients with chronic schizophrenia, reinforcing evenamide’s potential as a transformative therapy in treatment-resistant and poorly responding patients, offering a promising alternative to traditional dopamine D2-based antipsychotics.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41386-025-02188-y
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a long-term mental health condition that causes a range of different psychological symptoms. It is one of the most common serious mental health conditions. About 1 in 100 people will experience schizophrenia in their lifetime, with many continuing to lead normal lives. Schizophrenia is most often diagnosed between the ages of 15 and 35. Men and women are affected equally. There is no single test for schizophrenia. It is most often diagnosed after an assessment by a mental health care professional, such as a psychiatrist. It is important to diagnose schizophrenia as early as possible, as the chances of recovery improve the earlier it is treated. Schizophrenia is often described in terms of positive and negative (or deficit) symptoms. Positive symptoms are those that most individuals do not normally experience but are present in people with schizophrenia. They can include delusions, disordered thoughts and speech, and tactile, auditory, visual, olfactory and gustatory hallucinations, typically regarded as manifestations of psychosis. Hallucinations are also typically related to the content of the delusional theme. Positive symptoms generally respond well to medication. Negative symptoms are deficits of normal emotional responses or of other thought processes and are less responsive to medication.
Schizophrenia: high medical need for 20 million patients worldwide
Useful Links
Schizophrenia International Research Society (SIRS)
The Johns Hopkins Schizophrenia Center
The European Psychiatric Association
Xadago® (safinamide) is a New Chemical Entity for the treatment of Parkinson’s Disease with a mode of action characterized by selective MAO-B-inhibition. Results from two double-blind, placebo-controlled, multinational, 6 month studies with over 1,100 patients revealed that safinamide provides statistically significant increases in ON-time without troublesome dyskinesia, as well as a decrease in OFF-time. Safinamide requires a once-daily dose and has no diet restrictions due to its high MAO-B versus MAO-A selectivity.
Xadago®: 1st New Chemical Entity Approved in a Decade for Parkinson's Disease

References:
Mov Disord. 2014 Feb;29(2):229-37.
Randomized trial of safinamide add-on to levodopa in Parkinson's disease with motor fluctuations.
Borgohain R, et al
JAMA Neurol. 2017 Feb 1;74(2):216-224.
Assessment of safety and efficacy of safinamide as a levodopa adjunct in patients with parkinson disease and motor fluctuations: a randomized clinical trial.
Schapira AH et al
Significant Commercial Opportunity in Xadago® (Safinamide)
Parkinson’s disease (PD)
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common chronic progressive neurodegenerative disorder in the elderly after Alzheimer’s disease, affecting 1-2% of individuals aged ≥ 65 years worldwide. It is estimated that more than four million people in the industrialized countries suffer from PD. The prevalence of the PD market is expected to grow in the next years due to the increase in the global population and advancements in healthcare that contribute to an aging population at increased risk for PD. The diagnosis of PD is mainly based on observational criteria of muscular rigidity, resting tremor, or postural instability in combination with bradykinesia. As the disease progresses, symptoms become more severe. L-dopa remains as the most effective treatment for PD, and over 75% of the patients with PD receive L-dopa. However, long-term treatment with L-dopa leads to seriously debilitating motor fluctuations, i.e. phases of normal functioning (ON-time) and decreased functioning (OFF-time). Therefore, as the disease progresses, additional medications are added on to L-dopa to help with management of these motor fluctuations.
References and Useful Links
The Michael J. Fox Foundation
European Parkinson's Disease Association
American Parkinson Disease Association
BMC Oertel. European Handbook of Neurological Management, Vol 1, Chapter 14 & 15, 2011.
Ralfinamide is a unique, well-tolerated New Chemical Entity that specifically targets voltage-gated sodium channels originating from Newron’s ion channel program and is developed for a rare neuropathic pain indication. It is believed to mediate its potent analgesic effect through the inhibition of sodium channels, including Nav 1.7, N-type Calcium channels and NMDA receptor. Newron is looking for partners to advance the program into potentially pivotal studies in orphan indications in neuropathic pain.
Ralfinamide-oral New Chemical Entity targeting orphan neuropathic pain
Neuropathic Pain (NP)
Neuropathic pain is a type of chronic pain initiated or caused by a primary lesion of nervous system. While epidemiological studies indicate the incidence of neuropathic pain is 1%, most experts conclude this figure is most certainly an underestimate. Conditions associated with a high incidence of neuropathic pain include diabetes (10%), post-herpetic neuralgia (25%) and others. Neuropathic pain does not respond well to conventional pain therapy and may worsen over time. Pain is felt when special nerve terminals called nociceptors are stimulated. Following peripheral nerve injury, changes occur in the nervous fibers transmitting non-nociceptive stimuli, leading to neuropathic pain. Among these changes is an irregular membrane excitability, substained by profound alteration in the pattern of the sodium channel expression, including up-regulation of certain channels not normally observed in nociceptors, and down-regulation of others, thereby causing the brain to recognize pain from sources not normally painful. Up to 7% to 8% of the population is affected, and in 5% of individuals it may be severe.
Useful links
The European Pain Federation
Pain Alliance Europe
International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP)
Partnering
To progress the development and maximise the potential value of its novel CNS compounds, Newron has entered into a number of strategic relationships with established pharmaceutical companies.
In January 2025 Newron and Myung In Pharm entered into a license agreement to develop, manufacture and commercialize evenamide in South Korea.
In December 2024 Newron signed a license agreement with EA Pharma (a subsidiary of Eisai Co., Ltd.) to develop, manufacture and commercialize evenamide in Japan and other designated Asian territories
In April 2017, Meiji Seika and Eisai entered into a collaboration for the development and commercialization of safinamide in Parkinson’s disease for Japan and Asia.
In May 2012, Newron entered a strategic collaboration and licence agreement with Italian chemical and pharmaceutical company, Zambon, for Newron’s lead compound safinamide in all territories of the world with the exclusion of Japan and certain Asian territories.
Since then, Newron has received significant success based regulatory milestone payments as well as customary royalty payments on future sales of safinamide in the licensed territories. Zambon has granted the commercialization rights to Supernus for the U.S., to Valeo Pharma for Canada, to Seqirus for Australia and New Zealand and to Medison for Israel.
In February 2012 Newron signed a license agreement with Meiji Seika Pharma Co., Ltd., covering the research, development, manufacturing, and marketing of safinamide in Japan and key Asian territories.
Newron is committed to developing novel therapies for patients with diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system. We are looking to build our portfolio of products through in-house efforts as well as licensing and acquiring novel CNS compounds at various stages of development.
Newron has proven expertise in developing novel CNS and orphan products having taken a number of programs through pre-clinical, clinical phases and to market.
We are seeking partners who can complement our in-house CNS development capabilities and who share our ambition to deliver effective treatments to patients living with debilitating neurodegenerative and or rare diseases. We have a promising pipeline of novel therapies and are looking to enter licensing or co-development agreements that will enable us to realize their full potential.
To further explore collaboration opportunities with Newron please contact us at [email protected].